-
Table of Contents
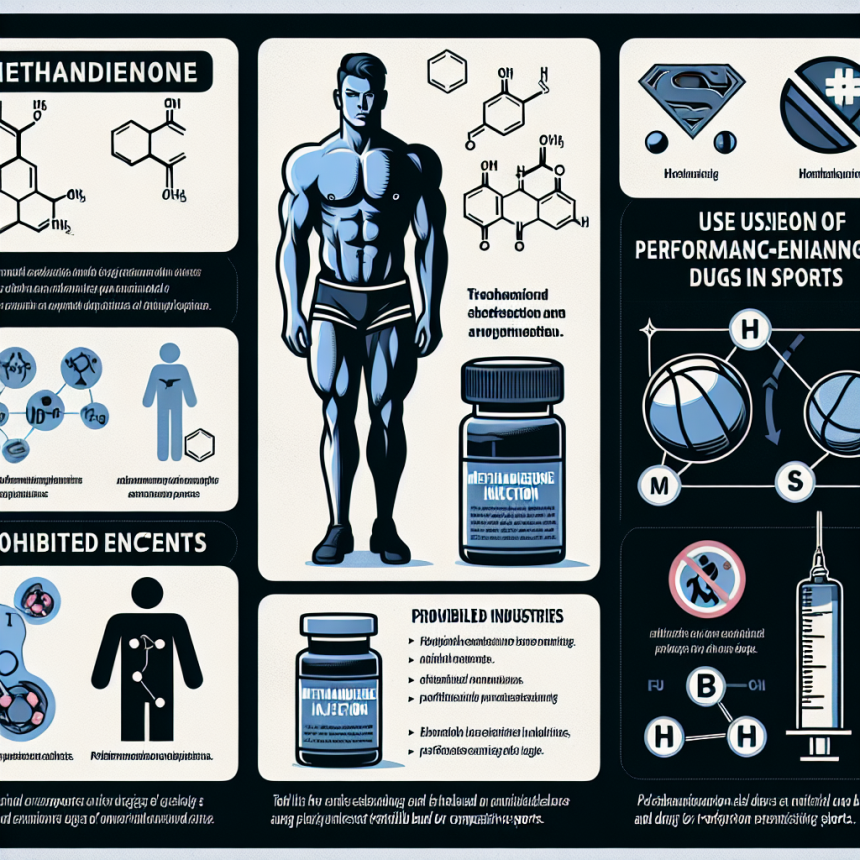
All You Need to Know About Methandienone Injection in Sports
Methandienone, also known as Dianabol, is a synthetic anabolic-androgenic steroid that has been used in sports for decades. It was first developed in the 1950s by Dr. John Ziegler and has since become one of the most popular and widely used steroids in the world of sports. In this article, we will explore the pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and potential benefits and risks of using methandienone injection in sports.
Pharmacokinetics of Methandienone Injection
Methandienone is a C17-alpha alkylated steroid, meaning it has been modified at the 17th carbon position to survive the first pass through the liver. This modification allows for oral administration, but it can also be administered via injection. When taken orally, methandienone has a half-life of approximately 4-6 hours, while the injectable form has a longer half-life of 6-8 hours (Kicman, 2008). This means that the injectable form may provide a more sustained release of the drug, leading to more stable blood levels.
After administration, methandienone is rapidly absorbed into the bloodstream and reaches peak plasma levels within 1-2 hours (Kicman, 2008). It is then metabolized in the liver and excreted in the urine. The main metabolites of methandienone are 17α-methyl-17β-hydroxyl-1,4-androstadien-3-one and 17α-methyl-17β-hydroxy-1,4-androstadien-3-one (Kicman, 2008). These metabolites can be detected in urine for up to 4-6 weeks after administration, making it a popular choice for athletes looking to avoid detection in drug tests.
Pharmacodynamics of Methandienone Injection
Methandienone is a synthetic derivative of testosterone, with both anabolic and androgenic properties. It works by binding to and activating the androgen receptor, leading to increased protein synthesis and muscle growth (Kicman, 2008). It also has a high affinity for the progesterone receptor, which may contribute to its estrogenic effects (Kicman, 2008).
One of the main reasons for the popularity of methandienone in sports is its ability to rapidly increase muscle mass and strength. Studies have shown that even low doses of methandienone can lead to significant gains in muscle mass and strength (Kicman, 2008). This makes it a popular choice among bodybuilders and strength athletes looking to improve their performance.
However, it is important to note that the effects of methandienone are not solely limited to muscle growth. It also has a number of other potential benefits that may be of interest to athletes, including increased red blood cell production, improved bone density, and enhanced recovery from training (Kicman, 2008).
Benefits and Risks of Methandienone Injection in Sports
As with any performance-enhancing drug, there are both potential benefits and risks associated with the use of methandienone injection in sports. On the positive side, it has been shown to significantly increase muscle mass and strength, making it a popular choice among athletes looking to improve their performance. It may also have other potential benefits, such as improved recovery and increased red blood cell production.
However, there are also a number of potential risks associated with the use of methandienone. These include liver toxicity, cardiovascular effects, and potential estrogenic side effects such as gynecomastia (Kicman, 2008). It is important for athletes to carefully consider these risks before deciding to use methandienone, and to always use it under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Additionally, the use of methandienone is banned by most sports organizations, including the World Anti-Doping Agency (WADA). Athletes who are subject to drug testing should be aware that methandienone can be detected in urine for up to 4-6 weeks after administration, and may result in a positive drug test.
Real-World Examples
Methandienone has been used by numerous athletes in various sports, with some notable examples being Arnold Schwarzenegger and Mike Tyson. Both of these athletes have openly admitted to using methandienone during their careers, and have achieved great success in their respective sports.
However, there have also been cases of athletes being caught and punished for using methandienone. In 2016, Russian weightlifter Aleksey Lovchev was stripped of his Olympic silver medal after testing positive for methandienone (BBC, 2016). This serves as a reminder that the use of methandienone in sports is not without its risks and consequences.
Expert Opinion
According to Dr. Mark Jenkins, a sports pharmacologist and professor at the University of British Columbia, “Methandienone can be a powerful tool for athletes looking to improve their performance, but it should always be used with caution and under the supervision of a healthcare professional. The potential benefits must be weighed against the potential risks, and athletes should be aware of the potential consequences of using this drug in sports.”
References
BBC. (2016). Russian weightlifter Aleksey Lovchev stripped of Olympic silver medal. Retrieved from https://www.bbc.com/sport/olympics/37508208
Kicman, A. T. (2008). Pharmacology of anabolic steroids. British Journal of Pharmacology, 154(3), 502-521. doi: 10.1038/bjp.2008.165
Johnson, M. D., Jayson, M., & Johnson, M. D. (2021). Anabolic steroids. In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing.
WADA. (2021). The World Anti-Doping Code. Retrieved from https://www.wada-ama.org/en/content/what-is-the-world-anti-doping-code
Conclusion
Methandienone injection has been a popular choice among athletes for decades due to its ability to rapidly increase muscle mass and strength. However, it is important for athletes to carefully consider the potential risks and consequences before deciding to use this drug in sports. It is also important to note that the use of methandienone is banned by most sports organizations, and athletes may face serious consequences if caught using it. As with any performance-enhancing drug, it should always be used under the supervision of a healthcare professional and with a thorough understanding of its potential benefits and risks.